RDF Dryer
Drying Systems use for refuse-derived fuel
RDF Dryer is designed to reduce moisture in shredded SRF (Solid Recovered Fuel) to below 20%, meeting strict requirements for cement kiln co-processing and enhancing calorific value for waste-to-energy plants. MSWsorting offers two advanced drying solutions: the Rotary Drum Dryer and the Belt Type Dryer. Both utilize low-temperature drying and ensure compliant exhaust gas control,
1. Rotary Drum Dryer for RDF/SRF Drying
Rotary Drum Dryer is a robust, continuous-processing dryer that uses a rotating cylindrical drum to tumble and dry shredded SRF materials. It is engineered for high-volume operations, efficiently handling large quantities of RDF with consistent moisture reduction. The system operates at low temperatures to preserve fuel quality while minimizing volatile emissions.

How It Works: Principle of Operation
Feeding & Tumbling: Wet SRF enters the drum through a controlled feeder. As the drum rotates slowly, internal flights (lifters) lift and cascade the material, exposing it uniformly to the heat stream.
Heat Transfer: Hot air or flue gas (sourced from waste heat or low-emission burners) flows co-currently or counter-currently through the drum. The tumbling action maximizes surface area for convective and conductive heat transfer, driving off moisture.
Moisture Evaporation & Separation: Evaporated moisture is carried by the gas stream into a downstream filtration unit (cyclone, bag filter, or scrubber). The dried RDF exits at the drum’s end, while exhaust gases are treated to meet environmental standards.
Control Systems: Advanced sensors monitor temperature, airflow, and moisture levels, allowing real-time adjustments for optimal drying efficiency.
Key Advantages & Features:
Low-Temperature Drying:Operates below 200°C (temperature optimized for specific RDF characteristics and moisture content), ensuring material integrity and safety.
Multi-Stage Drying Technology: Three-stage drying process (low-temperature preheating, main drying, and constant-temperature slow drying) minimizes plastic thermal shrinkage and fire risks.
Anti-Sticking Drum Coating: Specialized proprietary coating prevents material adhesion and buildup on drum interior surfaces.
Patented Lifting Flight Design: Advanced flight configuration repeatedly lifts and drops RDF to enhance material dispersion, maximize hot air contact, improve thermal efficiency, and prevent blockages.
Applications
Cement Plants: Large-scale RDF drying for kiln co-processing, where consistent low moisture (<20%) is critical for combustion stability.
Waste-to-Energy Facilities: Boosting calorific value (to 4,000–5,000 kcal/kg) of SRF for electricity generation.
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Processing Plants: Handling high throughputs (10–50 tonnes/hour) of heterogeneous waste streams.
Industrial Drying Projects: Suitable for bulky, irregular materials like shredded textiles, plastics, and biomass.
2. Belt Type Dryer for RDF/SRF Drying
Definition & Overview
Belt Type Dryer is a continuous conveyor-based system that dries SRF on a perforated belt while heated air circulates through the material bed. Designed for moderate throughputs, it offers precise control over drying parameters, making it ideal for sensitive or homogeneous fuel fractions. Like rotary dryers, it employs low-temperature drying and advanced exhaust gas treatment.
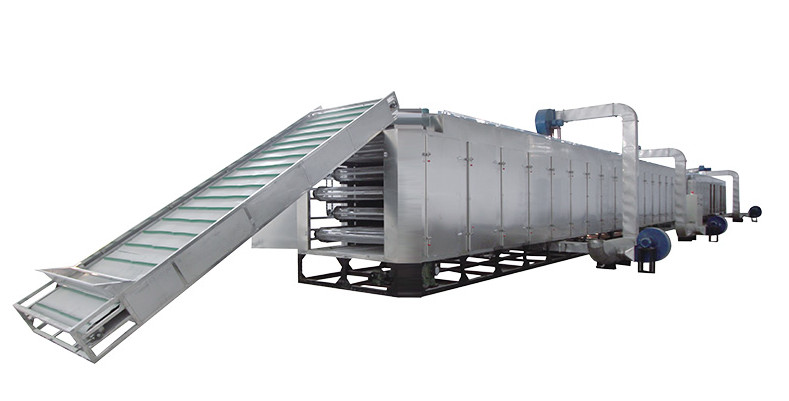

How It Works: Principle of Operation
Conveyorized Drying: Wet SRF is evenly spread on a slow-moving mesh belt, which travels through multiple temperature-controlled chambers (zones).
Zoned Heat Application: Each chamber has independent airflow and temperature settings. Heated air is forced upward or downward through the material layer, ensuring uniform moisture removal without overheating.
Staged Drying: The process typically includes preheating, constant-rate drying, and falling-rate drying stages. This gradual approach preserves material integrity and prevents over-drying.
Exhaust Management: Moisture-laden air is extracted, passed through condensers or biofilters, and recirculated to save energy. Final emissions are cleaned via scrubbers or thermal oxidizers.
Key Advantages & Features:
Ultra-Low Temperature Operation: Drying temperatures is low temperature significantly reduce fire hazards and minimize dust and pollutant emissions.
High Efficiency Drying: Large material surface exposure and optimized heat transfer achieve superior moisture reduction, product homogeneity, and higher calorific value.
Minimal Emissions Profile: Exceptionally low particulate emissions make this system ideal for regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Key Applications
Medium-Scale RDF Production: Plants processing 5–20 tonnes/hour of SRF, especially where feedstock uniformity is higher.
Specialized Waste Streams: Drying of pre-sorted commercial/industrial waste, packaging-derived fuels, or biomass pellets.
Sensitive Material Processing: Ideal for RDF with high plastic content, where excessive tumbling could cause agglomeration or degradation.
Retrofitting Existing Facilities: Modular design allows integration into space-constrained plants or hybrid drying lines.
Comparative Analysis: Rotary Drum vs. Belt Type Dryers
Aspect | Rotary Drum Dryer | Belt Type Dryer |
Throughput | High (10–50+ t/h) | Moderate (5–20 t/h) |
Material Handling | Handles heterogeneous, bulky SRF; tolerant of debris | Best for uniform, sized materials; gentle handling |
Footprint | Larger; requires more space | Compact; vertical designs available |
Energy Efficiency | High if using waste heat | Excellent with heat recirculation |
Moisture Control | Good; less precise for variable feedstocks | Excellent; zoned control for exact outcomes |
Maintenance | Higher mechanical wear (rotation parts) | Lower; easier belt access |
Choosing the Right Dryer for Your RDF/SRF Project
Choose Rotary Drum Dryer if:
Your facility processes high volumes of mixed MSW or SRF.
You prioritize throughput over precise moisture tuning.
Integration with cement kilns or large WtE plants is needed.
Waste heat (e.g., from kiln exhaust) is available for cost-effective drying.
Choose a Belt Type Dryer if:
Your feedstock is relatively uniform (e.g., pre-sorted commercial waste).
You require strict moisture control (±2%) for premium SRF markets.
Space is limited, or you need modular, scalable drying capacity.
Gentle drying is essential to preserve material structure and calorific value.
Enhancing RDF Quality with Advanced Drying
From an energy recovery and environmental perspective, drying waste to create RDF/SRF transforms a disposal problem into a resource. The high-calorific fuel can replace fossil fuels in industrial processes, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and landfill dependence. Furthermore, the drying process itself can be made energy-efficient by utilizing waste heat from other plant operations, such as flue gases from an on-site generator.
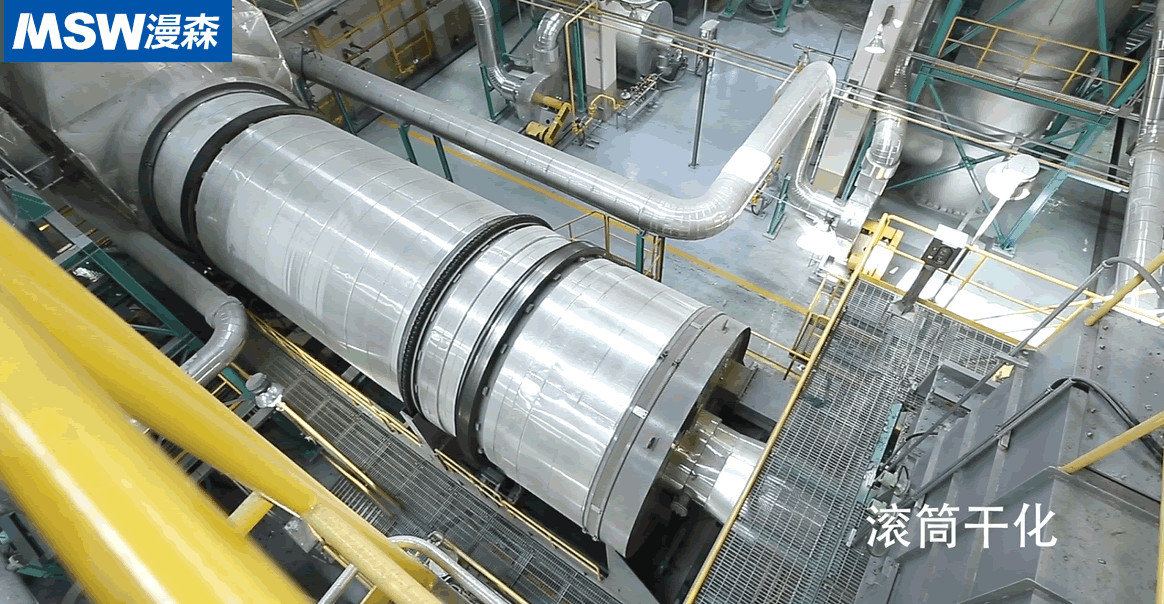
Both Rotary Drum and Belt Type Dryers from MSWsorting offer reliable, low-temperature solutions for reducing SRF moisture to under 20%. The Rotary Drum Dryer excels in high-capacity, rugged applications, while the Belt Type Dryer provides precision and flexibility for medium-scale operations. By selecting the appropriate system, waste processors can ensure compliance with cement kiln or WtE fuel specifications, maximize energy recovery, and contribute to circular economy goals.
For tailored advice on RDF drying solutions, consult with engineering experts of MSWsorting to match technology to your feedstock and output targets.
FLEXIBLE SORTING TECHNOLOGY AND SOLUTION

Manual Sorting Solutions
Belt ConveyorManual Sorting Room
For countries with low labor costs, a combination of mechanical and manual sorting can be used, which is a cost-effective waste sorting and recycling solution.
Read More
AI Robot Sorting Solutions
AI SortingSorting Robot
The artificial intelligence sorting robot with autonomous learning can practice and accumulate sorting data. It can effectively sort various high-value recyclables.
Read More
Optical Sorting Solutions
Optical Sorting
Optical sorter is a automatic sorting device based on sensors, high-speed ejector valve has large processing capacity. It is a good choice for bulk handling project of waste recycling.
Read More